Ovarian cysts are a common gynecological problem that affects women of reproductive age. They can be caused by various factors and can lead to a range of symptoms that vary in severity. Most ovarian cysts are functional, meaning they are related to the menstrual cycle and usually resolve on their own. However, some cysts can cause pain or other symptoms and may require medical treatment. Ovarian cysts can also be a symptom of conditions such as endometriosis or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
In this article, we will explore what ovarian cysts are, their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options like a medical or holistic approach to natural healing.
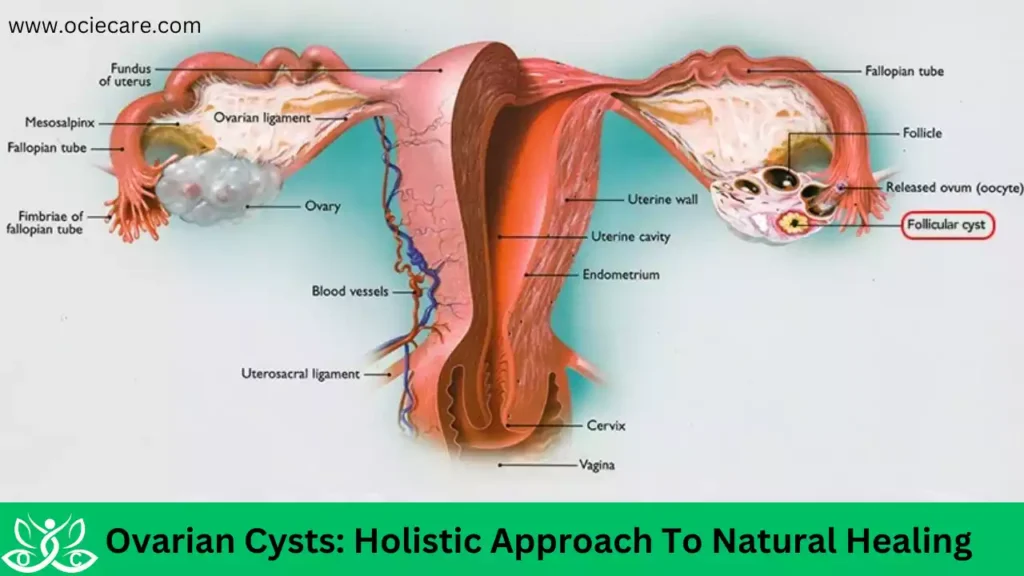
Ovarian Cysts
The Estimated Prevalence Of PCOs
The estimated prevalence of PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) and ovarian cysts in different regions is as follows:
I. Worldwide:
- PCOS affects women of reproductive age (15-49 years) globally.
- It has been reported to affect approximately 4% to 20% (equivalent to 8-40 crore) of women worldwide.
II. USA region:
- Ovarian cysts are relatively common among women in the United States.
- Studies have estimated that approximately 8% to 18% of women of reproductive age have ovarian cysts.
- However, the exact percentage may vary based on factors such as age, population group, and individual health conditions.
III. European region:
- In Europe, ovarian cysts are also relatively common.
- A large screening trial revealed a 21.2% incidence of ovarian cysts among healthy postmenopausal women.
- Prevalence rates may vary across different countries and populations within Europe.
III. African regions:
- Limited data is available specifically regarding the prevalence of ovarian cysts in African regions.
- In sub-Saharan Africa, there is limited data on the prevalence of PCOS, and different centers have quoted values ranging from 16% to 32%.
- Further research and specific studies are needed to determine the exact percentage of ovarian cyst cases in different African populations.
IV. Asian region:
- Like other regions, ovarian cysts are encountered among women in Asian countries.
- The prevalence rates can vary among different countries within the Asian region.
- Studies have indicated that the occurrence of ovarian cysts in Asian women is generally similar to the rates observed in the United States and Europe.
- In India specifically, the prevalence ranges from 3.7% to 22.5% (equivalent to 1.3-7.9 crore) of women.
However, it is worth noting that PCOS is not yet widely recognized as an important health problem worldwide.
It’s important to note that these percentages are general estimates and can vary depending on the population studied and the specific criteria used for diagnosis. For accurate and up-to-date information on the prevalence of ovarian cysts in each region, it is best to refer to published studies and data from reputable health organizations or consult healthcare professionals familiar with regional data.
What Are Ovarian Cysts?
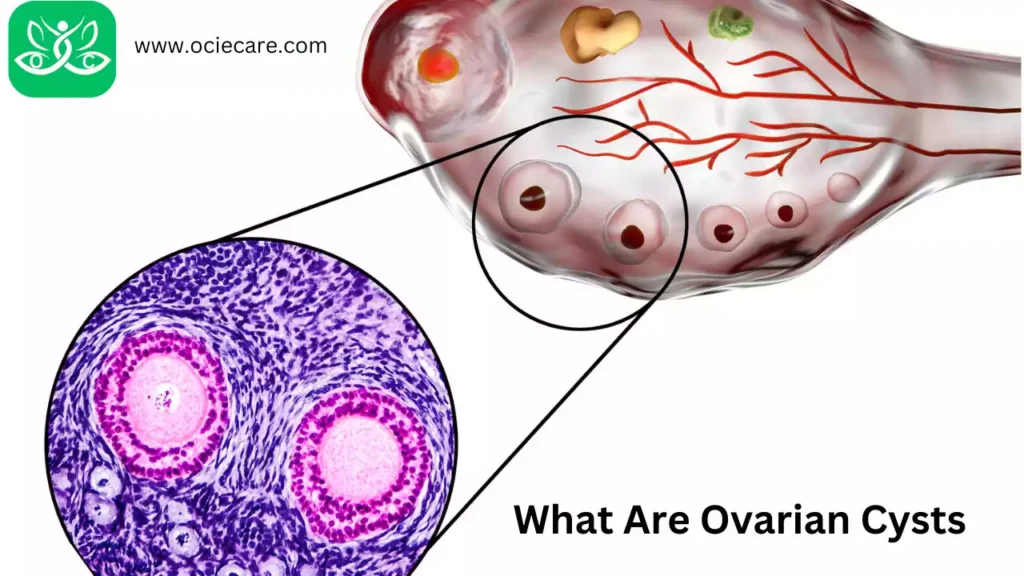
Ovarian cysts are abnormal growths fluid-filled sacs that develop in or on the ovaries, the reproductive organs in women. They can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous)vary in size, ranging from small, pea-sized cysts to larger ones that can reach several centimeters in diameter.
- Most ovarian cysts are functional cysts, meaning they develop as a normal part of the menstrual cycle and usually go away on their own.
- However, some cysts can cause complications and require medical intervention.
- An Ovarian cyst is a collection of fluids surrounded by a slender wall within the ovary.
- Ovarian cysts raise concern among many women, especially at childbearing age.
- While the majority of ovarian cysts are simply functional, some ovarian cysts can turn out to be cancerous.
- The first step in correctly diagnosing and treating ovarian cysts is to identify the cause of the disease. However, there is no single cause of ovarian cysts.
Know The Natural Solution of Uterine Fibroids In 21 Days
Types of Ovarian Cysts
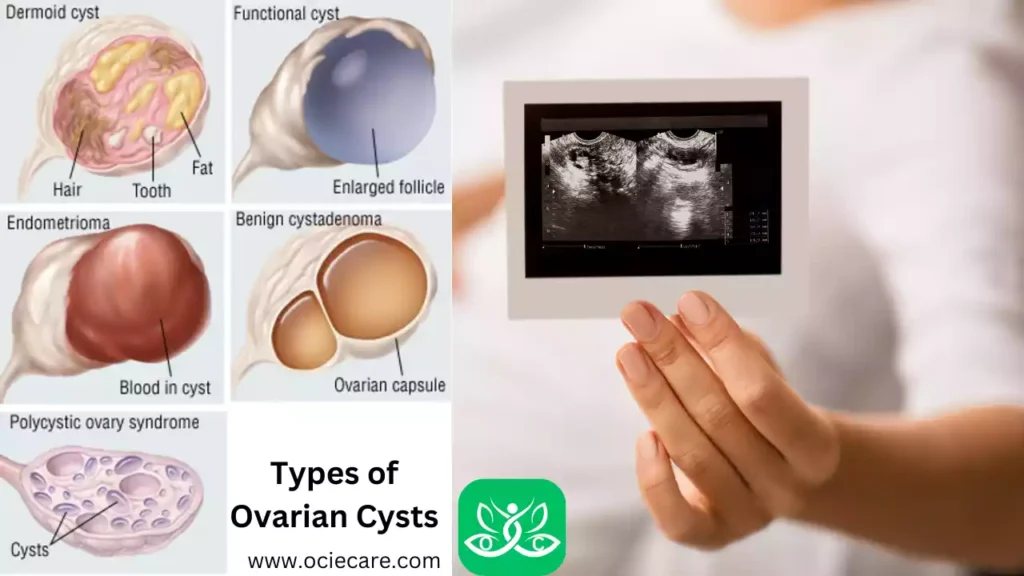
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop either within or on the surface of the ovaries. These cysts can vary in size and characteristics. Here are the common types of ovarian cysts:
I. Functional Cysts:
Functional cysts are the most common type of ovarian cysts and are typically related to the menstrual cycle. There are two subtypes of functional cysts:
a. Follicular Cysts:
- These cysts occur when a follicle fails to release an egg during ovulation. Instead, the follicle continues to grow and becomes a cyst.
- Follicular cysts usually resolve on their own within one to three menstrual cycles.
b. Corpus Luteum Cysts:
- After the release of an egg during ovulation, the follicle transforms into a structure called the corpus luteum.
- If the corpus luteum doesn’t dissolve as it should, it can fill with fluid and become a cyst.
- Corpus luteum cysts typically resolve on their own within a few weeks.
II. Dermoid Cysts:
- Dermoid cysts, also known as mature cystic teratomas, are a type of ovarian cyst that can contain various types of tissue.
- These cysts develop from cells that produce human eggs and can contain hair, skin, teeth, and even small sections of bone.
- Dermoid cysts are typically benign and may be present from birth but can become symptomatic later in life.
III. Endometriomas:
- Endometriomas, also called chocolate cysts, form when the tissue similar to the lining of the uterus (endometrium) grows within the ovary.
- These cysts are associated with endometriosis, a condition where endometrial tissue grows outside the uterus.
- Endometriomas can cause pain, inflammation, and fertility issues.
IV. Cystadenomas:
- Cystadenomas are cysts that develop from the outer surface of the ovary.
- They are typically filled with a watery or mucous-like fluid and can grow quite large.
- Cystadenomas can be categorized as serous cystadenomas or mucinous cystadenomas based on the type of fluid they contain.
- While most cystadenomas are benign, some may be cancerous (malignant).
V. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS):
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that can lead to the development of multiple small cysts on the ovaries.
- These cysts are usually small and can contribute to hormonal imbalances, irregular periods, and difficulties with ovulation.
It’s important to note that while most ovarian cysts are benign, some cysts can be cancerous or have the potential to become cancerous. Proper evaluation and diagnosis by a healthcare professional are necessary to determine the nature and appropriate management of ovarian cysts.
Causes of Ovarian Cysts
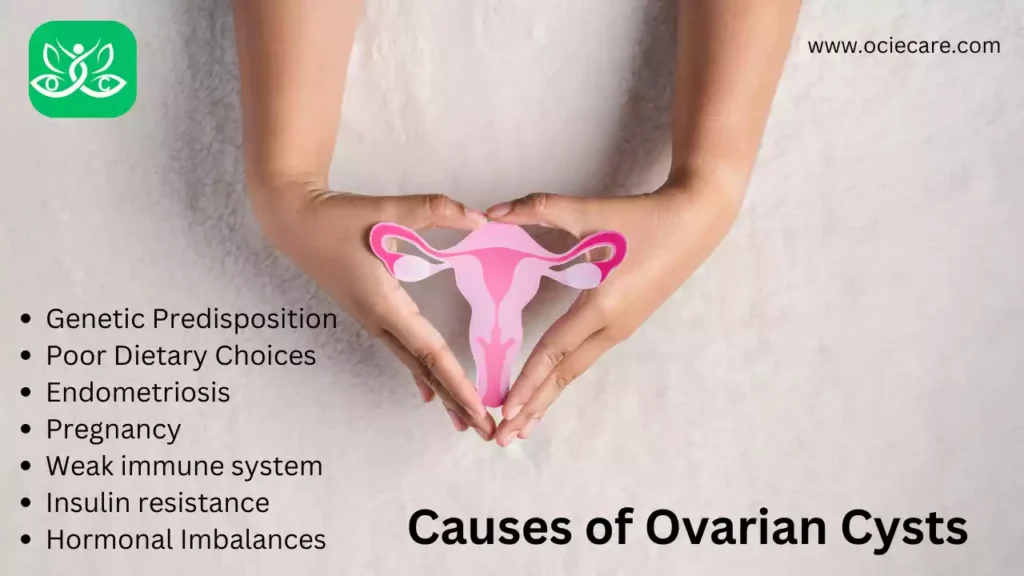
Ovarian cysts can develop for various reasons, and the exact cause can differ from woman to woman. Understanding the underlying factors that contribute to the formation of ovarian cysts is crucial in comprehending their nature and potential implications. Here are some common causes associated with ovarian cyst development:
I. Genetic Predisposition:
- In some cases, genetic factors can contribute to the development of ovarian cysts. Certain inherited conditions, such as multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) and basal cell nevus syndrome (Gorlin syndrome), can increase the likelihood of developing ovarian cysts.
- Genetic predisposition is often considered to be the primary cause of cysts as research has shown that the genetic pattern of women who suffer from this chronic condition is far different compared to women who have never suffered from cysts or PCOS.
- PCOS women are often predisposed to abnormal metabolism and dysfunctions of cell activity. Thus, Women who have had cysts in the past are more likely to develop them again.
- However, this should not be a death warrant as many times the genetic characteristics can be modified with the help of environmental factors and proper lifestyle-related changes.
II. Poor Dietary Choices:
- Different types of foods including refined carbohydrates, acidic foods, and foods that contain high levels of toxins and hormone-like substances can trigger hormonal imbalances such as those that occur during the menstrual cycle or due to conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can weaken your immune system making you more susceptible to cysts.
- Similarly, a diet rich in sugar and low on fresh vegetables can make the task of flushing out toxins difficult thereby aggravating your cysts condition
III. Endometriosis:
- Endometriosis is a condition where the tissue that lines the uterus (endometrium) grows outside the uterus, often on the ovaries.
- These endometrial implants can form cysts known as endometriomas or chocolate cysts. Endometriomas can cause pain and discomfort and are typically associated with infertility.
IV. Pregnancy:
- During pregnancy, a cyst called a corpus luteum cyst can form on the ovary. This cyst usually goes away on its own, but in rare cases, it can cause complications.
V. Weak immune system:
- Poor dietary choices, stress, and sleep deprivation can lead to a weakened immune system. A weakened immune system invites cannot defend the body against cyst formation.
VI. Insulin resistance:
- High levels of insulin can stimulate ovarian androgen production, which leads to the production of male hormones. This reduces the serum sex-hormone binding globulin or SHGB. The SHBG can in turn aggravate your cyst condition to quite an extent.
VII. Hormonal Imbalances:
- Imbalances in hormone levels can disrupt the normal ovulation process and contribute to the development of ovarian cysts.
- Hormonal conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can lead to the formation of multiple small cysts on the ovaries.
- In PCOS, the ovaries produce excessive amounts of androgens (male hormones) and have difficulty releasing eggs regularly, resulting in the accumulation of small cysts.
VIII. Other Factors:
- Additional factors that may play a role in ovarian cyst development include infertility issues, previous pelvic infections, and certain medical treatments such as hormonal stimulation used in assisted reproductive technologies.
- Age can also be a factor, as ovarian cysts are more common during the reproductive years.
- Besides the above primary factors, toxins in the liver and blood and even environmental toxins can increase the chances of cysts formation.
It’s important to note that while these factors are associated with the development of ovarian cysts, not all women with these factors will develop cysts, and some women without any known risk factors may still develop ovarian cysts. If you have concerns about ovarian cysts or are experiencing symptoms, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts

Ovarian cysts can present a variety of symptoms, although some women may not experience any symptoms at all. It’s important to note that the presence of these symptoms does not necessarily indicate the presence of ovarian cysts, as they can also be associated with other conditions.
If you are experiencing any of the following symptoms, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
I. Pelvic Pain or Discomfort:
- One of the most common symptoms of ovarian cysts is pelvic pain or discomfort. The pain can range from a dull, intermittent ache to a sharp, sudden sensation.
- It may occur on one side of the pelvis or both sides.
- The intensity of the pain can vary depending on the size and type of the cyst. Some women may experience pain during certain activities such as sexual intercourse or bowel movements.
II. Bloating and Abdominal Pressure:
- Ovarian cysts can cause bloating and a feeling of abdominal pressure.
- The abdomen may appear swollen or distended, and you may experience a sense of fullness or heaviness.
- This symptom is often described as similar to the discomfort felt during menstruation or when experiencing premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
III. Changes in Menstrual Patterns:
- Some women with ovarian cysts may notice changes in their menstrual cycles.
- These changes can include irregular periods, heavier or lighter bleeding than usual, or the absence of menstruation altogether.
- Ovarian cysts can disrupt the hormonal balance, affecting the regularity and characteristics of the menstrual cycle.
IV. Pain During Intercourse:
- Intercourse may become painful or uncomfortable for women with ovarian cysts.
- The presence of cysts can cause pressure or discomfort in the pelvic area, leading to pain during sexual activity.
- If you experience persistent pain during intercourse, it is important to discuss this symptom with your healthcare provider.
V. Frequent Urination:
- Large ovarian cysts can put pressure on the bladder, leading to increased frequency of urination.
- You may find yourself needing to urinate more frequently than usual or experiencing a sense of urgency even when the bladder is not full.
- If you notice a significant change in your urinary patterns, it is advisable to seek medical attention.
V. Difficulty Getting Pregnant:
- In some cases, cysts can interfere with ovulation and make it difficult to get pregnant.
It’s important to remember that these symptoms are not exclusive to ovarian cysts and can be caused by various other conditions. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms or have concerns about your reproductive health, it is recommended to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and proper diagnosis.
Know The Natural Treatment Of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Without Medicine
Diagnosis of Ovarian Cysts
Accurate diagnosis of ovarian cysts is essential to determine their characteristics, rule out potential complications, and guide appropriate treatment decisions. Healthcare professionals employ various diagnostic methods and techniques to evaluate ovarian cysts.
Here are some common approaches used in the diagnosis of ovarian cysts:
I. Medical History and Physical Examination:
- The diagnostic process usually begins with a comprehensive medical history assessment.
- Your healthcare provider will inquire about your symptoms, menstrual history, and any relevant medical conditions or previous surgeries.
- A physical examination, including a pelvic examination, may also be performed to assess the size, shape, and tenderness of the ovaries and to check for any associated pelvic abnormalities.
II. Imaging Techniques:
Imaging plays a crucial role in visualizing ovarian cysts and evaluating their characteristics. The following imaging techniques are commonly used:
a. Ultrasound:
- Transvaginal ultrasound is a common imaging modality for assessing ovarian cysts.
- It involves inserting a probe into the vagina to obtain detailed images of the ovaries and the cysts.
- Ultrasound helps determine the size, location, and structural features of the cysts, as well as their relationship with surrounding structures.
- It also helps distinguish between different types of cysts, such as simple cysts, complex cysts, or solid masses.
b. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging):
- In some cases, MRI may be utilized to provide more detailed images of the ovaries and cysts.
- MRI can help differentiate between benign and malignant cysts and provide additional information about their composition and characteristics.
III. Blood Tests:
Blood tests may be conducted to measure certain markers and hormones that can provide insights into the nature of ovarian cysts. These tests include:
a. CA-125 Test:
- CA-125 is a tumor marker that is often elevated in certain types of ovarian cysts, including cystadenomas and ovarian cancer. However, it is important to note that CA-125 levels can also be elevated in other non-cancerous conditions and may not be a definitive indicator of ovarian cancer.
b. Hormone Levels:
- Hormone levels, such as follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and estradiol, may be measured to evaluate hormonal imbalances that can contribute to cyst development, especially in cases of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
IV. Laparoscopy:
- Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that may be recommended for the diagnosis of ovarian cysts that are difficult to assess through imaging or for cases where there is a suspicion of malignancy.
- It involves making small incisions in the abdomen and inserting a thin, lighted instrument called a laparoscope.
- The laparoscope allows direct visualization of the ovaries and cysts, and if necessary, the surgeon can take a tissue sample (biopsy) for further analysis.
V. Additional Tests:
- Depending on the specific circumstances, additional tests may be required to aid in the diagnosis of ovarian cysts.
- These tests can include genetic testing, if there is a suspicion of an inherited genetic condition, or other imaging techniques such as CT scans or PET scans to evaluate the extent of the disease or rule out metastasis.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management of ovarian cysts. The choice of diagnostic method may vary based on individual factors, including the severity of symptoms, characteristics of the cysts, and the patient’s medical history.
Treatment of Ovarian Cysts

The treatment approach for ovarian cysts depends on various factors, including the type of cyst, its size, symptoms, and the individual’s age and reproductive plans. While many ovarian cysts resolve on their own without intervention, some may require treatment to alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, or address underlying conditions. Here are the common treatment options for ovarian cysts:
I. Watchful Waiting:
- If an ovarian cyst is small, asymptomatic, and determined to be a functional cyst or a benign condition, healthcare providers may recommend a watchful waiting approach.
- This involves monitoring the cyst through regular pelvic examinations and ultrasound imaging to ensure it resolves on its own without intervention.
- Watchful waiting is often the preferred approach for functional cysts that are expected to shrink and disappear within a few menstrual cycles.
II. Pain Management:
- For women experiencing pain or discomfort associated with ovarian cysts, pain management strategies may be recommended.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can help alleviate mild to moderate pain.
- In more severe cases, prescription pain medications may be prescribed for short-term use.
- Heat therapy, such as warm compresses or a heating pad, can also provide relief by relaxing the pelvic muscles and reducing pain.
III. Hormonal Birth Control:
- Hormonal birth control methods, such as combined oral contraceptives (containing estrogen and progestin) or progestin-only pills, may be prescribed to manage ovarian cysts.
- These medications work by preventing ovulation, reducing the formation of functional cysts, and regulating hormone levels.
- Hormonal birth control can help shrink existing cysts and prevent new ones from developing. It may also provide relief from symptoms such as pelvic pain, bloating, and menstrual irregularities.
IV. Surgical Interventions:
a. Ovarian Cystectomy:
- In cases where the cyst is large, causing severe symptoms, or suspected to be a complex cyst, a surgical procedure called ovarian cystectomy may be performed.
- During this procedure, the surgeon removes the cyst while preserving the unaffected ovarian tissue.
- Ovarian cystectomy is typically performed using minimally invasive techniques, such as laparoscopy, which involve making small incisions in the abdomen.
- In some instances, open surgery (laparotomy) may be necessary, especially for larger cysts or in cases where malignancy is suspected.
b. Oophorectomy:
- In rare cases where the cyst is cancerous (ovarian cancer), an oophorectomy may be recommended.
- This involves the surgical removal of one or both ovaries, along with the cyst. Depending on the stage and extent of the cancer, additional treatments such as chemotherapy may be required.
V. Follow-Up Monitoring:
- After treatment or during watchful waiting, follow-up monitoring is crucial to ensure the effectiveness of the chosen approach and to detect any recurrence or new cyst development.
- Regular pelvic examinations, ultrasound imaging, and blood tests (such as CA-125 levels) may be recommended to assess the status of the ovaries and monitor for any changes.
It is important for individuals with ovarian cysts to discuss their specific case with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable treatment option based on their unique circumstances. Treatment decisions may also be influenced by factors such as the individual’s age, desire for future fertility, and the presence of other medical conditions.
Understand About Blood Sugar | Diabetes, Treatment and Prevention
Potential Complications Associated with Ovarian Cysts
While many ovarian cysts are harmless and resolve on their own, some cysts can lead to complications that require medical attention. It’s important to be aware of the potential complications associated with ovarian cysts in order to seek prompt evaluation and treatment. Here are some possible complications:
I. Rupture:
- Ovarian cysts, particularly larger ones, can rupture or burst.
- This can cause sudden and severe abdominal or pelvic pain. Ruptured cysts can also lead to internal bleeding, which may require immediate medical intervention.
- Symptoms of a ruptured cyst may include sharp pain, dizziness, fainting, and rapid breathing.
- If you experience severe abdominal pain or suspect a cyst rupture, seek emergency medical care.
II. Torsion:
- Ovarian cysts, especially larger ones or those with a long stalk (pedunculated cysts), can twist or cause the ovary to twist.
- This condition is known as ovarian torsion. Torsion can lead to a disruption of blood flow to the ovary, causing intense abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
- Ovarian torsion is a medical emergency and requires immediate surgical intervention to untwist the ovary and prevent damage to the ovarian tissue.
III. Hemorrhage:
- In some cases, ovarian cysts can cause bleeding, either within the cyst itself or into the surrounding tissues.
- Hemorrhagic cysts, also known as blood-filled cysts, can lead to severe pelvic pain, heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, and fatigue.
- While most hemorrhagic cysts resolve on their own, significant bleeding may require medical evaluation and treatment.
IV. Infection:
- If an ovarian cyst becomes infected, it can lead to a condition called an ovarian abscess.
- This can occur when bacteria from the vagina or pelvic organs travel to the cyst and cause an infection.
- Symptoms of an ovarian abscess may include pelvic pain, fever, chills, and general malaise.
- Infection of an ovarian cyst usually requires antibiotics and, in severe cases, drainage or surgical intervention to remove the abscess.
V. Infertility:
- Certain types of ovarian cysts, such as endometriomas or large cysts that require surgical removal, can potentially impact fertility.
- Surgical procedures to remove cysts or the affected ovary may cause scarring or damage to the remaining ovarian tissue.
- Additionally, conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can disrupt normal ovulation and affect fertility.
- It’s important to discuss any concerns about fertility with a healthcare professional to explore appropriate management options.
VI. Malignancy:
- While most ovarian cysts are benign, some cysts can be cancerous or have the potential to develop into ovarian cancer.
- The risk of malignancy is generally low, but certain types of cysts, such as complex cysts or cysts with solid components, may raise concerns.
- If there is suspicion of malignancy based on imaging or other factors, further diagnostic tests or surgical interventions may be necessary to determine the nature of the cyst and guide appropriate treatment.
It’s important to remember that complications associated with ovarian cysts are relatively rare. However, if you experience severe or sudden abdominal pain, persistent symptoms, or any concerns about your reproductive health, it is crucial to seek medical attention for evaluation and appropriate management.
Regular gynecological check-ups and open communication with healthcare providers are key to early detection, timely treatment, and prevention of potential complications.
Preventive Measures for Ovarian Cysts
While it is not always possible to prevent the development of ovarian cysts, certain lifestyle choices and medical considerations may help reduce the risk or minimize the likelihood of complications. Here are some preventive measures and self-care practices that can be beneficial:
I. Regular Gynecological Check-ups:
- Schedule regular visits to your gynecologist for routine check-ups, even if you are not experiencing any symptoms.
- Regular pelvic examinations and ultrasound screenings can aid in the early detection and monitoring of ovarian cysts.
- These check-ups also allow for the evaluation of any other reproductive health concerns.
II. Birth Control Pills:
- Taking oral contraceptives or other hormonal birth control methods can help regulate hormonal imbalances and prevent certain types of ovarian cysts.
- Birth control pills work by preventing ovulation, reducing the risk of functional cysts.
- Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate type of contraceptive based on your specific needs and medical history.
III. Hormone Therapy:
- For women experiencing hormone imbalances or conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), hormone therapy may be recommended.
- Hormonal medications can help regulate the menstrual cycle, prevent the formation of cysts, and manage associated symptoms.
- It is important to discuss the potential benefits and risks of hormone therapy with your healthcare provider.
IV. Lifestyle Factors:
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can contribute to overall reproductive health. This includes:
a. Regular Exercise:
- Engaging in regular physical activity helps regulate hormone levels, reduce insulin resistance (which is associated with PCOS), and promote overall well-being.
- Consult with a healthcare professional to determine an exercise regimen suitable for your fitness level and any underlying medical conditions.
b. Balanced Diet:
- Eat a nutritious diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- This can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of hormonal imbalances and related conditions.
c. Weight Management:
- Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is important, particularly for women with PCOS.
- Weight loss, if necessary, can help regulate hormone levels and improve symptoms associated with PCOS.
d. Stress Management:
- High levels of stress can potentially disrupt hormonal balance.
- Engage in stress-reducing activities such as mindfulness practices, relaxation techniques, or engaging in hobbies that bring you joy.
V. Awareness of Symptoms:
- Be aware of the common symptoms of ovarian cysts, such as pelvic pain, bloating, changes in menstrual patterns, and pain during intercourse.
- Promptly report any persistent or concerning symptoms to your healthcare provider for evaluation and appropriate management.
VI. Genetic Counseling:
- If you have a family history of genetic conditions associated with ovarian cysts, consider seeking genetic counseling.
- Genetic counseling can provide information about the risks, inheritance patterns, and potential preventive measures specific to your genetic background.
It is important to note that while these preventive measures can be helpful, they may not guarantee the complete prevention of ovarian cysts. Some cysts may still develop despite taking preventive measures. Regular medical check-ups and open communication with your healthcare provider are essential for early detection, proper diagnosis, and timely management of ovarian cysts or any other reproductive health concerns.
Holistic Approach To Natural Healing
The holistic approach to healing emphasizes the importance of treating the body as a whole, addressing the underlying causes of a condition, and restoring balance to promote overall well-being. When it comes to ovarian cysts, adopting a multidimensional holistic approach can offer a long-term and gentle solution without the potential side effects of medications or the need for surgery.
Here are some key elements of a holistic approach to treating and preventing ovarian cysts:
I. Dietary Changes:
- A crucial aspect of holistic healing is adopting a balanced and nutritious diet.
- Focus on consuming whole foods, including fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Avoid processed foods, excessive sugar, and refined carbohydrates.
- A diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals supports hormonal balance and overall reproductive health.
- Additionally, drinking an adequate amount of water and reducing caffeine intake can promote detoxification and help maintain proper hydration.
II. Herbal Remedies and Supplements:
- Certain herbs and supplements have been traditionally used to support reproductive health and hormonal balance.
- Herbal remedies such as chasteberry, black cohosh, and evening primrose oil may be beneficial in regulating the menstrual cycle and reducing symptoms associated with ovarian cysts.
- However, it is important to consult with a qualified herbalist or healthcare provider before starting any herbal remedies or supplements to ensure safety and efficacy.
III. Stress Reduction and Emotional Well-being:
- Chronic stress can disrupt hormonal balance and contribute to the development or exacerbation of ovarian cysts.
- Incorporate stress-reduction techniques into your daily routine, such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or engaging in activities that promote relaxation.
- Taking care of your emotional well-being through practices like therapy, counseling, or support groups can also be beneficial in managing stress and promoting overall health.
IV. Exercise and Physical Activity:
- Regular physical activity plays a vital role in maintaining hormonal balance, managing weight, and promoting overall well-being.
- Engage in activities that you enjoy, such as walking, swimming, yoga, or dancing, for at least 30 minutes a day.
- Exercise helps improve blood circulation, reduce stress, and support the body’s natural detoxification processes.
V. Hormonal Balance:
- Balancing hormones is a key factor in treating and preventing ovarian cysts.
- Explore natural methods to regulate hormones, such as maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, and avoiding exposure to endocrine-disrupting substances found in certain plastics, pesticides, and personal care products.
- In some cases, hormone-balancing therapies, including bioidentical hormone replacement therapy, may be considered.
- Consult with a knowledgeable healthcare provider to explore appropriate options for your specific needs.
VI. Regular Check-ups and Monitoring:
- Even with a holistic approach, it is important to continue regular gynecological check-ups and monitoring to ensure proper evaluation and management of ovarian cysts.
- Work with a healthcare provider who supports and understands the holistic approach, as they can provide guidance, monitor your progress, and adjust treatment plans as necessary.
Remember that the holistic approach to healing takes into account your unique circumstances and aims to restore balance to the body as a whole. It is essential to consult with qualified healthcare professionals who specialize in holistic and integrative medicine to develop a personalized treatment plan that aligns with your needs and goals.
In this way, the holistic approach to treating cysts offers a long-term, safe, and gentle solution without the side effects of drugs or the risk of surgery while ensuring the prevention of future ovarian recurrence.
This article has a reference to the book, “Ovarian Cyst Miracle” by Carol Foster. Carol is an author, researcher, nutritionist, and health consultant who dedicated her life to creating the ultimate holistic ovarian cyst solution guaranteed to permanently cure all types of cysts and dramatically improve the overall quality of your life, naturally, without the use of prescription medication or surgery, and any side effects.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can develop within or on the surface of the ovaries. While most ovarian cysts are benign and resolve on their own, some may cause symptoms or lead to complications. Common symptoms include pelvic pain, bloating, changes in menstrual patterns, pain during intercourse, and frequent urination. Diagnostic methods such as medical history assessment, physical examinations, ultrasound imaging, and blood tests are used to evaluate ovarian cysts.
Treatment options vary depending on the type, size, and symptoms of the cysts. Watchful waiting, pain management, hormonal therapies, and surgical interventions like cystectomy or oophorectomy may be employed. Regular check-ups and monitoring are important to ensure proper evaluation, management, and prevention of future cysts.
The holistic approach to healing emphasizes treating the body as a whole, addressing underlying causes, and restoring balance. Dietary changes, herbal remedies, stress reduction techniques, regular exercise, and hormonal balance are key elements of a holistic approach to treating and preventing ovarian cysts. However, it is crucial to consult with qualified healthcare professionals to develop personalized treatment plans.
Remember, while some preventive measures can reduce the risk of ovarian cysts, it may not be possible to prevent all cysts. Early detection, prompt medical attention, and regular gynecological check-ups are essential for proper evaluation and management. By adopting a comprehensive approach, individuals can make informed decisions about their reproductive health and well-being.
FAQs
Q. What are ovarian cysts?
A. Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop within or on the surface of the ovaries. They can vary in size and may be categorized into different types, including functional cysts, dermoid cysts, endometriomas, and cystadenomas.
Q. What are the symptoms of ovarian cysts?
A. The symptoms of ovarian cysts can vary, but common signs include pelvic pain or discomfort, bloating, changes in menstrual patterns, pain during intercourse, and frequent urination. However, some cysts may not cause any noticeable symptoms and are incidentally discovered during routine check-ups or medical imaging scans.
Q. Are all ovarian cysts cancerous?
A. No, the majority of ovarian cysts are benign, meaning they are not cancerous. However, some cysts can be cancerous or have the potential to develop into ovarian cancer. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and to determine the nature of the cyst.
Q. How are ovarian cysts diagnosed?
A. Ovarian cysts are typically diagnosed through a combination of medical history assessment, physical examinations, and imaging techniques. Transvaginal ultrasound is commonly used to visualize the ovaries and cysts. Blood tests, such as CA-125 levels, may also be performed to evaluate certain markers and hormone levels associated with ovarian cysts.
Q. Can ovarian cysts affect fertility?
A. In some cases, ovarian cysts can impact fertility. Large cysts or those causing hormonal imbalances, such as in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), may disrupt normal ovulation and affect fertility. Surgical removal of cysts or ovaries can also potentially affect reproductive capabilities. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized evaluation and guidance.
Q. How are ovarian cysts treated?
A. The treatment of ovarian cysts depends on various factors, including the type of cyst, its size, symptoms, and the individual’s medical history. Treatment options can range from watchful waiting and pain management to hormonal therapies or surgical interventions, such as cystectomy or oophorectomy. The chosen treatment approach will be tailored to the specific needs and circumstances of each individual.
Q. Can ovarian cysts come back after treatment?
A. There is a possibility of ovarian cysts recurring after treatment, especially in cases of certain underlying conditions like PCOS. Regular monitoring and follow-up evaluations are important to detect any potential recurrence or new cyst development. Consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate management and ongoing care.
Q. Are there any natural remedies for ovarian cysts?
A. Certain natural remedies, such as dietary changes, herbal supplements, stress reduction techniques, and regular exercise, may complement conventional treatment approaches for ovarian cysts. However, it is important to consult with a qualified healthcare provider before incorporating any natural remedies to ensure safety and efficacy.
Q. When should I seek medical attention for ovarian cysts?
A. It is advisable to seek medical attention if you experience severe or sudden abdominal pain, persistent symptoms, or concerns about your reproductive health. Additionally, if you experience symptoms such as fever, vomiting, or signs of cyst rupture, immediate medical attention should be sought.
Q. Can ovarian cysts be prevented?
A. While it may not be possible to prevent all ovarian cysts, certain lifestyle choices, such as maintaining a healthy weight, adopting a balanced diet, managing stress, and regular gynecological check-ups, may help reduce the risk or minimize complications associated with ovarian cysts. Consulting with healthcare professionals who specialize in holistic and integrative medicine may provide additional insights on preventive measures.


Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.