Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas, are noncancerous growths that develop in the uterus. These benign tumors can vary in size and location within the uterus, and they affect a significant number of women worldwide. While uterine fibroids are generally not life-threatening, they can cause a range of bothersome symptoms and have a significant impact on a woman’s quality of life.
In this article, we will explore natural solutions for managing uterine fibroids, providing you with valuable insights into alternative approaches to treatment.

Uterine Fibroids
Prevalence Of Uterine Fibroids
The exact prevalence of uterine fibroids is difficult to determine, as many women with fibroids may remain asymptomatic and never seek medical attention. However, it is estimated that approximately 20-80% of women will develop fibroids by the age of 50. They are more prevalent among African-American women and tend to occur at an earlier age and with greater severity.
What Is Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas, are noncancerous growths that develop in the uterus, specifically within the muscular wall of the uterus or attached to it. These growths are composed of smooth muscle cells and fibrous connective tissue.
Uterine fibroids are a prevalent health concern among women, particularly those in their reproductive years. These growths develop from the smooth muscle tissue of the uterus and can range in size from tiny seedlings to large masses that distort the shape of the uterus. The exact cause of fibroids is still unknown, but various factors contribute to their development.
Types Of Uterine Fibroids
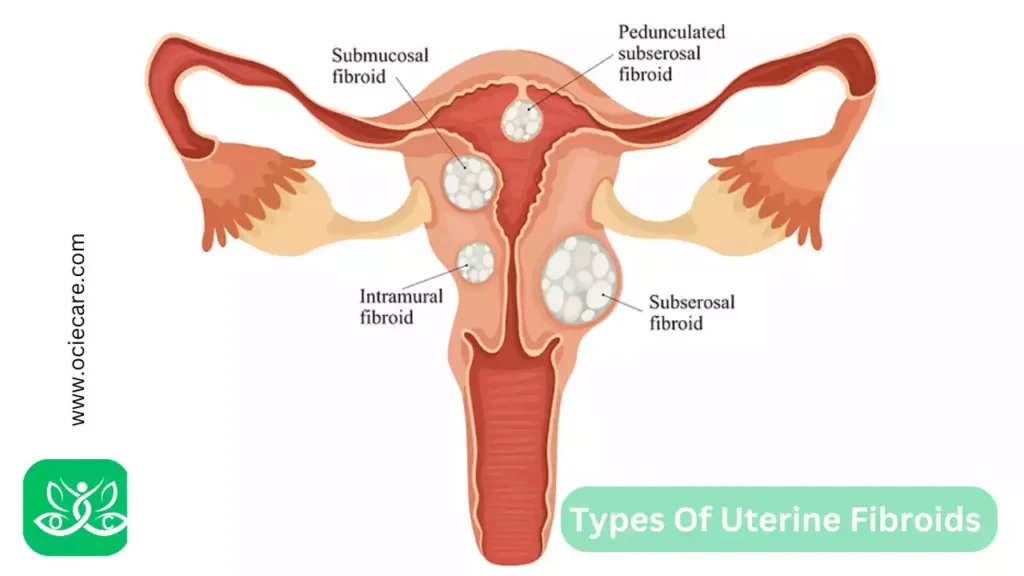
There are several types of uterine fibroids, classified based on their location within the uterus:
I. Intramural Fibroids:
- These are the most common type and develop within the muscular wall of the uterus.
- They can cause the uterus to enlarge and may lead to symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and pressure.
II. Submucosal Fibroids:
- These fibroids grow just underneath the lining of the uterus and can protrude into the uterine cavity.
- They are associated with heavy and prolonged menstrual bleeding and may contribute to infertility and miscarriages.
III. Subserosal Fibroids:
- These fibroids develop on the outer surface of the uterus and can grow outward, causing the uterus to enlarge.
- While they may not significantly affect menstrual bleeding, they can lead to pelvic pain and pressure.
IV. Pedunculated Fibroids:
- These fibroids are attached to the uterus by a stalk or peduncle.
- They can either be submucosal or subserosal in location. Depending on the size and location, they may cause symptoms similar to the corresponding types mentioned above.
Know The Natural Treatment Of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Without Medicine
Causes and Risk Factors Of Uterine Fibroids
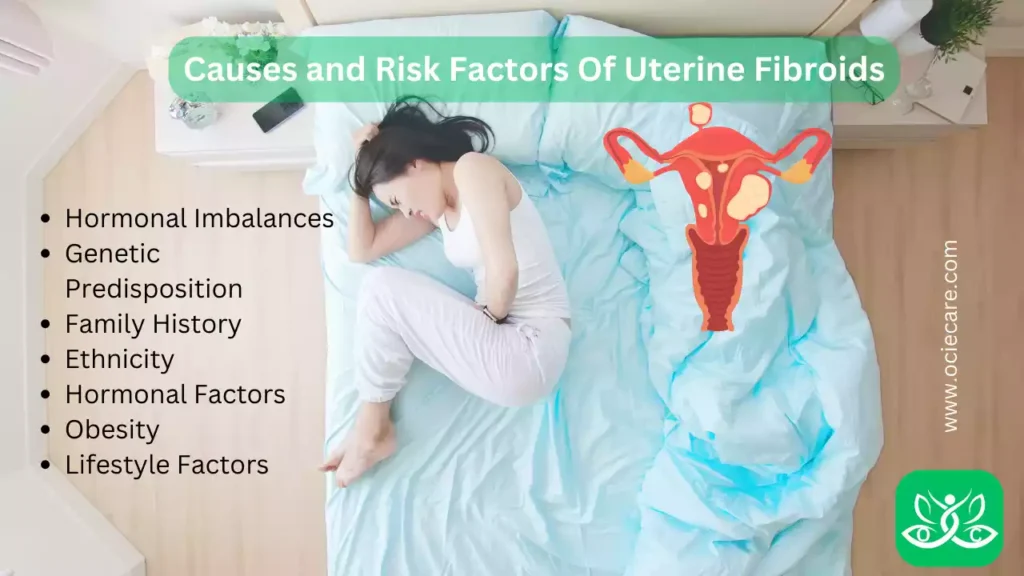
The exact cause of uterine fibroids is still not fully understood. However, several factors have been identified that may contribute to their development. These factors include:
I. Hormonal Imbalances:
- Hormones, particularly estrogen, and progesterone, are believed to play a significant role in the growth of uterine fibroids.
- Estrogen, in particular, stimulates the growth of the uterine lining during each menstrual cycle.
- Higher levels of estrogen have been associated with an increased risk of developing fibroids.
II. Genetic Predisposition:
- Uterine fibroids tend to run in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition to their development.
- If a woman’s mother or sister has had fibroids, she may be at a higher risk of developing them herself.
III. Family History:
- In addition to genetic factors, a family history of uterine fibroids can increase the likelihood of developing them.
- The specific genes involved in fibroid development are still being investigated.
IV. Ethnicity:
- Uterine fibroids are more prevalent among certain ethnic groups, particularly women of African descent.
- They tend to occur at an earlier age, grow larger, and cause more severe symptoms in these populations.
V. Hormonal Factors:
- Other hormonal factors, such as the early onset of menstruation (before the age of 10), late menopause (after the age of 55), and the use of hormonal contraceptives, may influence the development of uterine fibroids.
VI. Obesity:
- There is evidence to suggest that obesity is associated with an increased risk of developing uterine fibroids.
- Higher levels of body fat can lead to higher estrogen levels, which may contribute to fibroid growth.
VII. Lifestyle Factors:
- Certain lifestyle factors, such as a sedentary lifestyle and a diet high in red meat and low in fruits and vegetables, have been associated with an increased risk of uterine fibroids.
It is important to note that while these factors may increase the risk of developing uterine fibroids, they do not guarantee their occurrence. Many women with one or more of these risk factors never develop fibroids, and some women without any known risk factors may develop them.
Understanding the causes and risk factors of uterine fibroids can help in the prevention and management of these growths. Regular check-ups, maintaining a healthy weight, and adopting a balanced diet may contribute to reducing the risk of developing uterine fibroids or managing their symptoms effectively.
It is advisable to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance based on individual circumstances.
Common Symptoms Of Uterine Fibroids
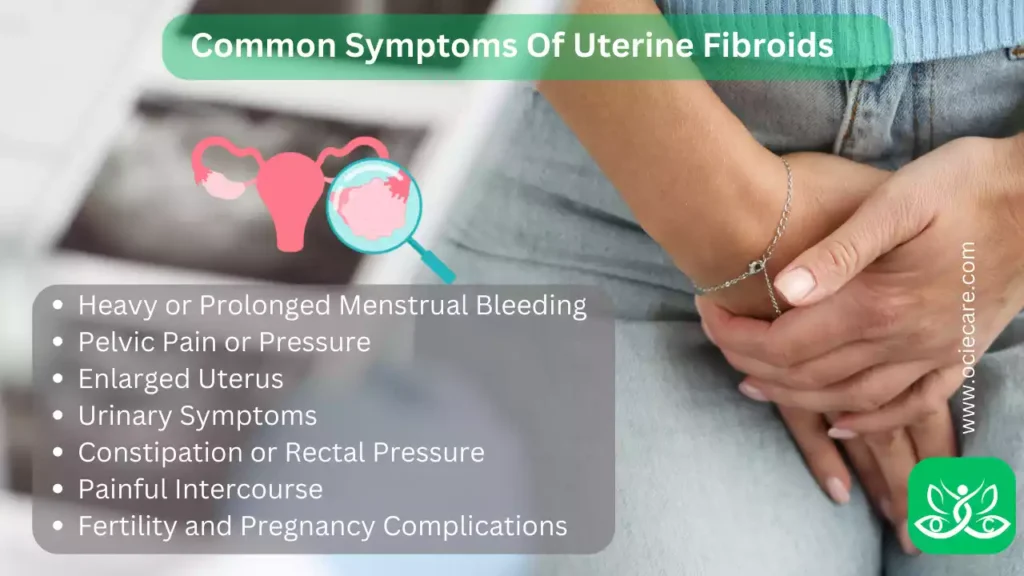
Uterine fibroids can cause a variety of symptoms, although some women may remain asymptomatic and only discover the presence of fibroids during routine pelvic examinations or imaging tests. When symptoms do occur, they can vary in severity and may include:
I. Heavy or Prolonged Menstrual Bleeding:
- One of the most common symptoms of uterine fibroids is heavy menstrual bleeding, also known as menorrhagia.
- Women may experience prolonged periods lasting longer than usual, with an increased flow of blood.
- This can lead to the need for frequent changing of sanitary protection, and in some cases, it may result in anemia.
II. Pelvic Pain or Pressure:
- Fibroids can cause pelvic pain or discomfort.
- The pain may be dull or sharp and can vary in intensity.
- It may be constant or intermittent and may worsen during menstruation.
- Fibroids can also cause a sensation of pressure or fullness in the pelvic area.
III. Enlarged Uterus:
- Depending on the size and number of fibroids, the uterus may become enlarged.
- This can lead to a visible increase in abdominal size or a feeling of bloating.
- In some cases, the enlarged uterus may be palpable during a pelvic examination.
IV. Urinary Symptoms:
- Large fibroids that press against the bladder can lead to urinary symptoms.
- Women may experience increased frequency of urination, a frequent urge to urinate, or difficulty emptying the bladder.
- In rare cases, fibroids can obstruct the flow of urine, leading to urinary retention.
V. Constipation or Rectal Pressure:
- Fibroids located near the back of the uterus can press against the rectum, causing symptoms such as constipation or a sensation of rectal pressure.
VI. Painful Intercourse:
- In some instances, fibroids can cause pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse (dyspareunia).
- The pain may be experienced deep in the pelvis or during certain positions.
VII. Fertility and Pregnancy Complications:
- Depending on their size and location, fibroids can interfere with fertility by affecting the implantation of a fertilized egg or blocking the fallopian tubes.
- They can also increase the risk of complications during pregnancy, such as miscarriage, preterm labor, or a higher likelihood of needing a cesarean section.
It’s important to remember that the severity and presence of symptoms can vary greatly among women with uterine fibroids. Some may experience mild symptoms that do not significantly impact their daily lives, while others may have more severe symptoms that require medical intervention.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms or have concerns about uterine fibroids, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management options.
Diagnosing Methods Of Uterine Fibroids
Diagnosing uterine fibroids typically involves a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examination, and imaging tests. These methods help healthcare providers assess the size, location, and number of fibroids present.
The following are the commonly used diagnostic methods for uterine fibroids:
I. Medical History Evaluation:
- The healthcare provider will begin by taking a detailed medical history, including questions about the patient’s symptoms, menstrual cycle, and any relevant family history of fibroids or other reproductive conditions.
II. Physical Examination:
- A pelvic examination is performed to assess the size, shape, and position of the uterus.
- The healthcare provider may be able to feel enlarged or irregular areas that could indicate the presence of fibroids.
III. Transvaginal Ultrasound:
- This imaging test uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the uterus.
- During a transvaginal ultrasound, a small probe is inserted into the vagina to obtain detailed images of the uterus and any fibroids present.
- This method helps in determining the size, number, and location of fibroids.
IV. Pelvic MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging):
- MRI provides detailed images of the uterus and surrounding structures.
- It can help differentiate between fibroids and other conditions, as well as provide more precise information about the size, location, and characteristics of the fibroids.
- MRI is especially useful in cases where fibroids are complex or difficult to assess by other methods.
V. Hysteroscopy:
- In this procedure, a thin, lighted tube with a camera (hysteroscope) is inserted through the vagina and cervix into the uterus.
- It allows direct visualization of the uterine cavity and any fibroids that may be present.
- Hysteroscopy can help identify submucosal fibroids that protrude into the uterine cavity.
VI. Saline Sonohysterogram:
- This test involves the injection of sterile saline solution into the uterus through the cervix.
- The saline helps expand the uterine cavity, making it easier to visualize any abnormalities, including submucosal fibroids, using transvaginal ultrasound.
VII. Biopsy:
- In rare cases where there is suspicion of malignancy (cancerous growth), a biopsy may be performed.
- A small tissue sample is collected from the fibroid or the lining of the uterus and sent to a laboratory for further examination.
These diagnostic methods help healthcare providers accurately diagnose uterine fibroids and assess the need for treatment. The choice of diagnostic tests may vary depending on the individual patient’s symptoms, physical examination findings, and healthcare provider’s judgment.
It is important to consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management options based on the specific circumstances of each individual.
Treatment Options For Uterine Fibroids
The choice of treatment for uterine fibroids depends on several factors, including the severity of symptoms, the desire for future fertility, and the size, number, and location of the fibroids. Treatment options can range from conservative approaches to surgical interventions.
The following are the various treatment options available for uterine fibroids:
I. Watchful Waiting:
- If fibroids are small, asymptomatic, and do not affect a woman’s quality of life, a watchful waiting approach may be adopted.
- Regular monitoring and check-ups with a healthcare provider are recommended to ensure any changes or new symptoms are detected.
II. Medications:
Medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms or temporarily shrink the size of fibroids.
These may include:
a. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs):
- NSAIDs such as ibuprofen or naproxen can help alleviate pain associated with fibroids and reduce menstrual bleeding.
b. Hormonal Therapies:
- Hormonal treatments, such as birth control pills, may be prescribed to regulate the menstrual cycle and reduce heavy bleeding.
- Other hormonal options include progestin-releasing intrauterine devices (IUDs) or gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists, which can temporarily induce a menopausal state and shrink fibroids.
III. Minimally Invasive Procedures:
These procedures aim to treat fibroids while preserving the uterus. They are typically recommended for women who desire future fertility or prefer to avoid major surgery.
Some common minimally invasive procedures include:
a. Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE):
- In UAE, tiny particles are injected into the uterine arteries to block the blood supply to the fibroids.
- This causes them to shrink and reduces associated symptoms.
b. Magnetic Resonance-guided Focused Ultrasound Surgery (MRgFUS):
- This procedure uses focused ultrasound waves to heat and destroy the fibroid tissue while leaving the surrounding structures unharmed.
c. Radiofrequency Ablation:
- Radiofrequency energy is used to heat and destroy the fibroid tissue.
- This procedure is performed via a small needle-like device that is inserted into the fibroid under ultrasound guidance.
IV. Surgical Interventions:
In more severe cases or when fertility is not a concern, surgical interventions may be recommended. These procedures involve the removal of the fibroids or, in some cases, the entire uterus. Surgical options include:
a. Myomectomy:
- Myomectomy involves the surgical removal of fibroids while preserving the uterus.
- It can be performed through various approaches, including abdominal, laparoscopic, or hysteroscopic methods.
b. Hysterectomy:
- Hysterectomy is the complete removal of the uterus. It may be recommended for women who have severe symptoms, large or multiple fibroids, or do not desire future fertility.
V. Endometrial Ablation:
- This procedure involves the destruction or removal of the uterine lining (endometrium).
- It can help reduce heavy menstrual bleeding associated with fibroids but does not directly target or remove the fibroids themselves.
The choice of treatment depends on individual circumstances, and it is important to discuss the risks, benefits, and potential outcomes of each option with a healthcare provider. The decision-making process should consider the woman’s symptoms, desire for future fertility, and overall well-being. Regular monitoring and follow-up are crucial to ensure the effectiveness of the chosen treatment approach.
Natural Remedies | Alternative Therapies for Uterine Fibroids
While natural remedies, Alternative therapies, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications may not directly treat or eliminate uterine fibroids, they can potentially help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being.
It’s important to note that these approaches should be discussed with a healthcare provider and used as complementary strategies alongside medical treatments.
Here are some natural remedies, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications that may be beneficial for managing uterine fibroids:
I. Herbal Remedies:
Certain herbs have been traditionally used to alleviate symptoms associated with fibroids. Examples include:
a. Chasteberry (Vitex):
- Chasteberry may help regulate hormonal imbalances and reduce symptoms like heavy bleeding and pelvic pain.
b. Dong Quai:
- Dong Quai is believed to have estrogen-like effects and may help regulate hormone levels and manage menstrual irregularities.
c. Milk Thistle:
- Milk Thistle has anti-inflammatory properties and may support liver health, potentially aiding in hormone metabolism.
It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before using herbal remedies, as they can interact with medications and may not be suitable for everyone.
II. Nutritional Modifications:
Although there is limited scientific evidence linking specific dietary factors to the development or management of uterine fibroids, adopting a healthy, well-balanced diet may support overall health and potentially alleviate symptoms.
Consider the following dietary modifications:
a. Increase Fiber Intake:
- Consuming fiber-rich foods, such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes, may help reduce estrogen levels in the body and promote regular bowel movements.
b. Choose Healthy Fats:
- Opt for healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish.
- These fats have anti-inflammatory properties and can support hormone balance.
c. Limit Processed Foods and Added Sugars:
- Processed foods and added sugars may contribute to inflammation and hormonal imbalances. Minimize their consumption and focus on whole, unprocessed foods.
d. Consider Phytoestrogens:
- Phytoestrogens are naturally occurring compounds found in certain foods, such as soybeans, flaxseeds, and legumes.
- They may help regulate estrogen levels in the body.
III. Stress Management:
- Chronic stress can disrupt hormonal balance and contribute to inflammation.
- Engaging in stress-reducing practices such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies and activities that promote relaxation can be beneficial.
IV. Regular Exercise:
- Engaging in regular physical activity can help maintain a healthy weight, promote circulation, and reduce symptoms associated with fibroids.
- Choose activities you enjoy, such as walking, swimming, cycling, or dancing, and aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
V. Heat Therapy:
- Applying a heating pad or taking warm baths can help alleviate pelvic pain and discomfort associated with fibroids.
VII. Acupuncture:
- Some women find acupuncture helpful for symptom management, although the scientific evidence is limited.
- Acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to promote balance and healing.
VIII. Homeopathy:
- Homeopathy is a system of medicine that uses highly diluted substances to stimulate the body’s natural healing processes.
- Specific homeopathic remedies may be prescribed based on individual symptoms and constitutional factors.
- The effectiveness of homeopathy for fibroids is not well-established, and more research is needed.
IX. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM):
- TCM involves various therapies, such as herbal medicine, acupuncture, dietary modifications, and lifestyle recommendations.
- TCM practitioners may tailor treatments based on the individual’s specific pattern of symptoms and overall health.
- Some herbal formulations and acupuncture protocols are used in TCM for managing uterine fibroids.
X. Mind-Body Techniques:
- Stress reduction techniques and mind-body approaches, such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises, may help manage symptoms associated with fibroids.
- These practices can promote relaxation, reduce stress levels, and improve overall well-being.
It is crucial to remember that natural remedies, Alternative therapies, and lifestyle modifications may vary in effectiveness for each individual. It is always advisable to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new natural remedies or making significant dietary or lifestyle changes.
A healthcare provider can provide personalized guidance and ensure the chosen strategies align with your specific needs and overall treatment plan.
Ovarian Cysts: Holistic Approach To Natural Healing
Pregnancy and Uterine Fibroids
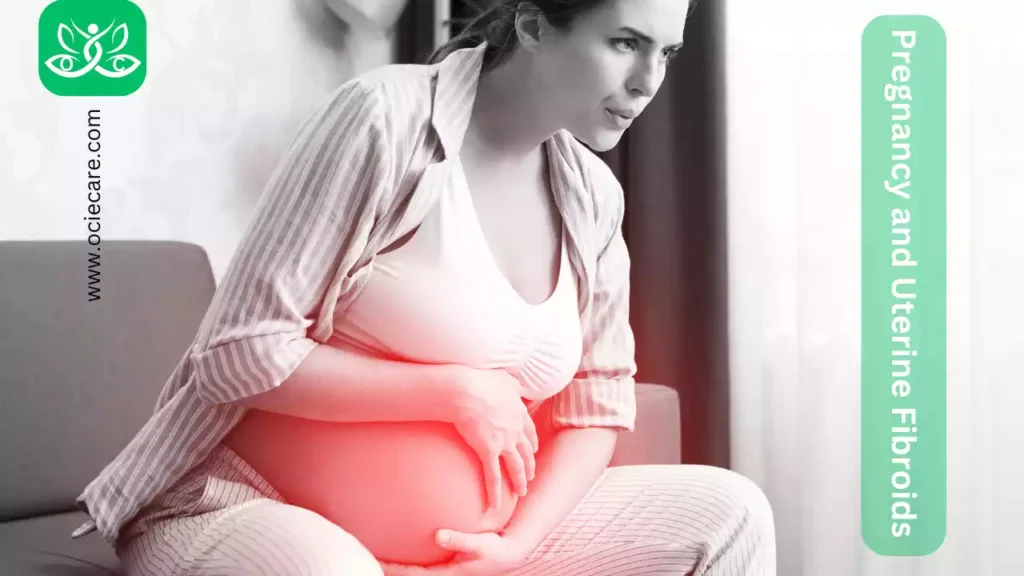

Uterine fibroids can have an impact on pregnancy and fertility, and the management of fibroids during pregnancy requires careful consideration.
Here’s an overview of their impact and management:
A. Impact on Pregnancy:
I. Increased Risk of Miscarriage:
- Depending on their size and location, fibroids can increase the risk of miscarriage, especially if they are near the placenta or interfere with the implantation of the fertilized egg.
II. Preterm Birth:
- Large or multiple fibroids can increase the risk of preterm birth (delivering the baby before 37 weeks of gestation).
- Fibroids may cause the uterus to stretch prematurely or disrupt the normal process of labor.
III. Placental Abruption:
- In rare cases, fibroids can lead to the separation of the placenta from the uterine wall before delivery, known as placental abruption.
- This can cause bleeding, and abdominal pain, and can be a life-threatening complication.
B. Impact on Fertility:
I. Submucosal Fibroids:
- Submucosal fibroids that protrude into the uterine cavity can interfere with implantation and may reduce fertility.
II. Fallopian Tube Blockage:
- Large fibroids near the fallopian tubes may block or distort the tubes, hindering the fertilization process.
C. Management of Fibroids during Pregnancy:
I. Monitoring:
- Regular monitoring is crucial to assess the growth and position of fibroids during pregnancy.
- Ultrasound examinations are typically used to evaluate the size and location of fibroids and to monitor the baby’s development.
II. High-Risk Pregnancy Care:
- If fibroids pose a risk to the pregnancy, a woman may receive specialized care from a healthcare provider experienced in high-risk pregnancies.
- This may involve more frequent check-ups, monitoring of fetal well-being, and specific interventions based on individual circumstances.
III. Treatment Considerations:
- Most fibroids do not require treatment during pregnancy, as they often do not cause significant issues.
- However, if complications arise, treatment options may include pain management, hormonal therapy, or, rarely, surgery.
- The decision for intervention depends on the severity of symptoms, potential risks to the mother or baby, and the stage of pregnancy.
It’s important for women with fibroids who are planning to conceive or are already pregnant to discuss their condition with a healthcare provider. The healthcare provider can provide individualized guidance, monitor the fibroids throughout pregnancy, and ensure appropriate management to optimize the chances of a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
After pregnancy, fibroids may naturally shrink, particularly after menopause, as estrogen levels decrease. However, some women may require further treatment if fibroid-related symptoms persist or worsen.
Understand The Menopause The Revolutionary 21-Day Program for Women
Surgical Procedures and Interventional Radiology To Treat Uterine Fibroids
There are various surgical procedures and interventional radiology techniques available to treat uterine fibroids. The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the severity of symptoms, desire for future fertility, size, number, and location of fibroids, as well as the patient’s overall health.
Here’s detailed information about some commonly used surgical procedures and interventional radiology techniques for treating uterine fibroids:
A. Myomectomy:
Myomectomy is a surgical procedure performed to remove fibroids while preserving the uterus. There are different approaches to myomectomy:
I. Abdominal Myomectomy:
- A larger incision is made in the lower abdomen to access and remove fibroids.
II. Laparoscopic Myomectomy:
- Several small incisions are made in the abdomen, and specialized surgical instruments are used to remove the fibroids.
III. Hysteroscopic Myomectomy:
- A hysteroscope, a thin tube with a camera, is inserted through the vagina and cervix into the uterus.
- The fibroids are visualized and removed using specialized instruments.
Myomectomy is often preferred for women who wish to preserve their fertility or maintain the uterus. It can effectively alleviate symptoms caused by fibroids.
B. Hysterectomy:
Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus. It can be performed through different approaches:
I. Abdominal Hysterectomy:
- A larger incision is made in the lower abdomen to remove the uterus.
II. Vaginal Hysterectomy:
- The uterus is removed through an incision made in the vagina.
III. Laparoscopic Hysterectomy:
- Several small incisions are made in the abdomen, and the uterus is removed using specialized instruments.
Hysterectomy is typically recommended for women who have severe symptoms, large or multiple fibroids or do not desire future fertility. It provides a definitive solution for fibroids but eliminates the possibility of future pregnancies.
C. Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE):
UAE is an interventional radiology procedure that involves blocking the blood supply to the fibroids by injecting tiny particles into the uterine arteries. This causes the fibroids to shrink and alleviates associated symptoms.
- UAE is a minimally invasive procedure that can be effective in managing fibroids without surgery.
- It preserves the uterus, making it an option for women who desire future fertility.
- It may not be suitable for women planning to conceive soon, as there is a potential risk of decreased fertility after the procedure.
D. Magnetic Resonance-guided Focused Ultrasound Surgery (MRgFUS):
MRgFUS uses focused ultrasound waves to heat and destroy the fibroid tissue while leaving surrounding structures unharmed. It is guided by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to ensure precise targeting.
- MRgFUS is a noninvasive procedure that does not require incisions.
- It provides an alternative to surgery for women who wish to preserve their uterus.
- However, it may not be suitable for all fibroid types and sizes, and its availability may be limited.
E. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA):
RFA is a minimally invasive procedure that uses radiofrequency energy to heat and destroy fibroid tissue. A thin needle-like device is inserted into the fibroid under ultrasound guidance.
- RFA can be performed on an outpatient basis and may be suitable for certain fibroid types and sizes.
- It is a relatively newer technique, and its long-term effectiveness is still being evaluated.
It’s important for individuals to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment option based on their specific circumstances and treatment goals.
The healthcare provider will consider factors such as symptom severity, desire for future fertility, and overall health to guide the decision-making process.
Importance of Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Consulting a healthcare professional for uterine fibroids is crucial for several reasons:
I. Accurate Diagnosis:
- A healthcare professional can accurately diagnose uterine fibroids through a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examination, and imaging tests.
- They can differentiate fibroids from other conditions that may have similar symptoms, ensuring an accurate diagnosis.
II. Individualized Treatment Plan:
- Every woman’s situation is unique, and a healthcare professional can develop an individualized treatment plan based on the severity of symptoms, desire for future fertility, and the size, number, and location of fibroids.
- They can discuss various treatment options and help make informed decisions.
III. Expert Guidance:
- A healthcare professional can provide expert guidance throughout the treatment process.
- They can explain the benefits, risks, and potential outcomes of different treatment options, enabling individuals to make informed choices based on their specific circumstances.
IV. Monitoring and Follow-up:
- Regular monitoring is essential to assess the growth and changes in fibroids.
- A healthcare professional can provide the necessary follow-up care, monitor symptoms, and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
V. Fertility Considerations:
- Uterine fibroids can impact fertility and pregnancy outcomes.
- A healthcare professional can assess the impact of fibroids on fertility and provide guidance on treatment options that are compatible with future reproductive goals.
VI. Management During Pregnancy:
- If a woman with fibroids becomes pregnant, a healthcare professional can closely monitor the condition and manage any potential complications.
- They can ensure optimal care for both the mother and the developing baby.
VII. Comprehensive Care:
- Uterine fibroids can have a significant impact on a woman’s physical and emotional well-being.
- A healthcare professional can provide comprehensive care, addressing not only the physical symptoms but also the emotional aspects of living with fibroids.
VIII. Safety and Risk Management:
- Some treatment options for uterine fibroids carry risks and potential complications. Consulting a healthcare professional ensures that the chosen treatments are safe and appropriate for the individual’s specific circumstances.
- They can provide guidance on managing risks and potential side effects.
Overall, consulting a healthcare professional ensures that individuals receive accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, expert guidance, and ongoing monitoring and care. It is important to have open and honest communication with a healthcare professional to address concerns, ask questions, and receive the necessary support throughout the journey of managing uterine fibroids.
Uterine Fibroids – The Natural Solution In 21 Days
Uterine Fibroids – The Natural Solution” is a concise and informative guide designed to empower women who are seeking a natural approach to address uterine fibroids. Written with clarity and compassion, this book provides a comprehensive introduction to uterine fibroids, which are non-cancerous growths that develop in the uterus.
The book begins by explaining the causes, symptoms, and potential complications associated with uterine fibroids. It emphasizes the importance of understanding the condition and its impact on a woman’s physical and emotional well-being.
This book will treat you naturally on the following:
- Treat all types and sizes of fibroids quickly, naturally, and safely
- Prevent heavy periods, bleeding, cramping, and clotting permanently
- Treat the pain and bloating associated with Uterine Fibroids
- Get rid of excessive weight
- Become more relaxed and enjoy excellent sleep
- Treat most digestive disorders
- Feel lighter, healthier, look younger, and more energetic.
- Experience enhanced elimination, clockwork periods, thicker hair, and healthier skin and nails
- Have increased mental clarity, enthusiasm, and vitality.
- Save thousands of dollars and avoid the costs and consequences of surgery.
Unlike conventional medical treatments that often involve surgery or medication, this guide focuses on natural solutions that promote holistic healing. It delves into various natural remedies, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies that can alleviate symptoms and support uterine health.
Throughout the book, readers will find practical advice on dietary modifications, herbal remedies, stress management techniques, and exercises specifically tailored for uterine fibroids. The author emphasizes the importance of self-care and provides tools to help women take charge of their health journey.
Moreover, “Uterine Fibroids – The Natural Solution” acknowledges the significance of seeking professional guidance and encourages readers to work collaboratively with healthcare providers. It emphasizes the complementary nature of natural approaches and conventional medical treatments, advocating for an integrative approach to achieve optimal outcomes.
This book aims to empower women by providing them with knowledge, tools, and resources to make informed decisions about their health. It promotes a holistic and natural approach to managing uterine fibroids, fostering hope and empowering women to take control of their well-being.
Fibroids Miracle™
The Only Holistic Fibroid System In Existence That Will Show YOU How To Quickly and Permanently treatment
Your Uterine Fibroids, End The Chronic Pain, Rebalance Your Body and Achieve PERMANENT Freedom From All Hormonal Related Disorders!
This book was written by “Amanda Leto, a Medical researcher, health consultant, nutrition specialist, and author of the
Fibroids Miracle™ system.
Conclusion
In conclusion, uterine fibroids are common noncancerous growths that develop in the uterus. They can vary in size, number, and location within the uterus. The exact cause of fibroids is unknown, but factors such as hormonal imbalances, genetic predisposition, family history, and certain ethnic backgrounds may contribute to their development.
Uterine fibroids can cause a range of symptoms, including heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain or pressure, urinary symptoms, constipation, and fertility issues. However, not all women with fibroids experience symptoms, and some may remain asymptomatic.
When seeking diagnosis and treatment for uterine fibroids, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional. They can accurately diagnose fibroids, assess the severity of symptoms, and develop an individualized treatment plan based on factors such as symptom severity, desire for future fertility, and the characteristics of the fibroids.
Treatment options include watchful waiting, medication to manage symptoms, minimally invasive procedures (such as uterine artery embolization, focused ultrasound surgery, or radiofrequency ablation), surgical interventions (such as myomectomy or hysterectomy), and lifestyle modifications.
Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, herbal remedies, and mind-body techniques, may provide additional support in managing symptoms, but their effectiveness varies and should be used in conjunction with medical advice.
Consulting a healthcare professional is vital throughout the process of managing uterine fibroids. They provide accurate diagnosis, expert guidance, individualized treatment plans, monitoring, and follow-up care. They can also address fertility considerations, manage fibroids during pregnancy, and ensure comprehensive care for physical and emotional well-being.
By working collaboratively with a healthcare professional, individuals with uterine fibroids can make informed decisions, receive appropriate treatment, and achieve optimal management of their condition. Regular communication and follow-up care are key to effectively managing uterine fibroids and improving the overall quality of life.
FAQs
Q. What are uterine fibroids?
A. Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths that develop in the uterus. They are composed of muscle and fibrous tissue and can vary in size, number, and location.
Q. What are the symptoms of uterine fibroids?
A. The symptoms of uterine fibroids can vary, but common ones include heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain or pressure, urinary symptoms, constipation, and fertility issues.
Q. How are uterine fibroids diagnosed?
A. Uterine fibroids are diagnosed through a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examination, and imaging tests such as ultrasound, MRI, or hysteroscopy.
Q. What causes uterine fibroids?
A. The exact cause of uterine fibroids is unknown, but hormonal imbalances, genetic factors, family history, and certain ethnic backgrounds may contribute to their development.
Q. Are uterine fibroids cancerous?
A. Uterine fibroids are almost always noncancerous (benign). However, in rare cases, a cancerous fibroid called leiomyosarcoma can occur.
Q. Can uterine fibroids cause infertility?
A. Uterine fibroids can sometimes interfere with fertility. Depending on their size and location, they can affect implantation or block the fallopian tubes. However, not all fibroids cause infertility.
Q. How are uterine fibroids treated?
A. Treatment options for uterine fibroids include watchful waiting, medication, minimally invasive procedures (such as uterine artery embolization or focused ultrasound surgery), surgical interventions (like myomectomy or hysterectomy), and lifestyle modifications.
Q. What are the non-surgical treatment options for uterine fibroids?
A. Non-surgical treatment options include medication to manage symptoms, uterine artery embolization (UAE), magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound surgery (MRgFUS), and radiofrequency ablation (RFA).
Q. What is a myomectomy?
A. A myomectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of fibroids while preserving the uterus. It can be performed through different approaches, such as abdominal, laparoscopic, or hysteroscopic methods.
Q. What is a hysterectomy?
A. A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the uterus. It can be performed abdominally, vaginally, or laparoscopically. Depending on the specific case, the cervix, and ovaries may also be removed.


Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.